crm accounting is changing the way businesses handle financial operations and customer relationships. By combining the power of customer relationship management with accounting functions, companies can now achieve a seamless integration that saves time, reduces errors, and maximizes growth opportunities. Imagine tracking all your invoices, payments, and customer data from a single platform—crm accounting makes it a reality for modern businesses of all sizes.
This approach links sales, customer service, and finance teams, ensuring everyone works from the same up-to-date information. Features like automated invoicing, real-time payment tracking, and customizable dashboards help businesses improve efficiency and gain deeper insights into their financial health. With the added benefits of security, compliance, and scalability, crm accounting is quickly becoming the go-to solution for organizations looking to stay ahead in a competitive marketplace.
Introduction to CRM Accounting
Customer Relationship Management (CRM) accounting combines the power of CRM platforms with financial management tools to deliver an integrated experience for modern businesses. This fusion enables organizations to coordinate customer information with accounting data, making workflows smoother and helping teams collaborate more efficiently.
CRM accounting solutions are especially significant today as businesses demand seamless operations between sales, support, and finance departments. By consolidating customer data, transaction histories, and financial activities, companies can improve their decision-making, provide more personalized service, and enhance overall profitability.
CRM Integration with Accounting Functions
CRM accounting systems operate by connecting traditional CRM capabilities—like contact management and sales tracking—with essential accounting tasks such as invoicing, payment processing, and financial reporting. This unification allows businesses to automate repetitive tasks, minimize manual errors, and ensure consistent, up-to-date records across all departments.
Objectives and Benefits of CRM Accounting
Integrating CRM with accounting software aims to provide end-to-end visibility of customer interactions and financial transactions. Some of the key benefits include:
- Streamlining workflows by reducing data silos and manual data entry.
- Automating tasks like invoice generation, payment follow-ups, and expense tracking.
- Enabling better forecasting and financial planning based on comprehensive customer and sales data.
- Improving customer satisfaction through timely billing, accurate statements, and responsive service.
Core Features of CRM Accounting Systems
CRM accounting systems come equipped with a set of core features that are designed to make business operations more effective and collaborative. These functionalities bridge the gap between customer relationship management and financial processes, offering a holistic view of each client’s journey and associated transactions.
Essential Features in CRM Accounting Solutions
The following table summarizes the main features commonly found in CRM accounting platforms, along with their descriptions, benefits, and practical example use cases.
| Feature | Description | Benefit | Example Use Case |
|---|---|---|---|
| Automated Invoicing | Automatically generates and sends invoices based on sales data and agreements. | Saves time and reduces manual errors, ensuring timely billing. | A recurring service provider schedules monthly invoices for subscription clients. |
| Payment Tracking | Monitors incoming payments and flags overdue accounts. | Improves cash flow and helps prioritize collection efforts. | A finance team instantly identifies late payments to send reminders. |
| Customer Data Management | Centralizes customer profiles with transaction history and account status. | Enhances personalization and service quality. | A support rep reviews recent purchases before responding to a client inquiry. |
| Financial Reporting | Provides real-time access to sales, revenue, and expense reports. | Enables better forecasting and strategic planning. | Management reviews monthly sales trends to adjust marketing strategies. |
Efficiency Through Automation
Features like automated invoicing and payment tracking not only save valuable time but also reduce financial errors that stem from manual processes. These tools allow businesses to maintain steady cash flows and deliver prompt financial communications to clients.
Interconnected Customer Data and Transaction History
By uniting customer data management and transaction histories, CRM accounting systems create a single source of truth. This centralization empowers teams to deliver more informed support, anticipate customer needs, and provide tailored solutions based on up-to-date financial activity.
CRM Accounting vs. Traditional Accounting Software
Businesses face a critical choice between adopting a CRM accounting system or sticking with standalone accounting software. Understanding the distinctions is essential for selecting the right solution for evolving business needs.
Differences Between Integrated and Standalone Systems
CRM accounting solutions merge customer-centric functions with accounting, while traditional accounting software typically focuses solely on financial management. This difference impacts how information is accessed, shared, and used throughout the organization.
Comparison of Advantages and Disadvantages
Below is a summary of the pros and cons of each approach:
- CRM Accounting Systems:
- Advantages: Unified data, streamlined sales-to-cash processes, improved customer communication, better reporting.
- Disadvantages: May require more complex setup, higher initial costs, or additional training for staff.
- Traditional Accounting Software:
- Advantages: Simpler for finance-only tasks, lower cost for basic needs, familiar to most accountants.
- Disadvantages: Siloed data, limited customer insight, manual handoffs between sales and finance teams.
Impact on Financial Workflows
For example, with a CRM accounting platform, a sales rep can instantly see a customer’s outstanding balance before finalizing a new order, reducing risk and ensuring faster collections. In contrast, traditional software would require separate communication between departments, delaying decisions and potentially missing revenue opportunities.
Integration of CRM and Accounting Modules
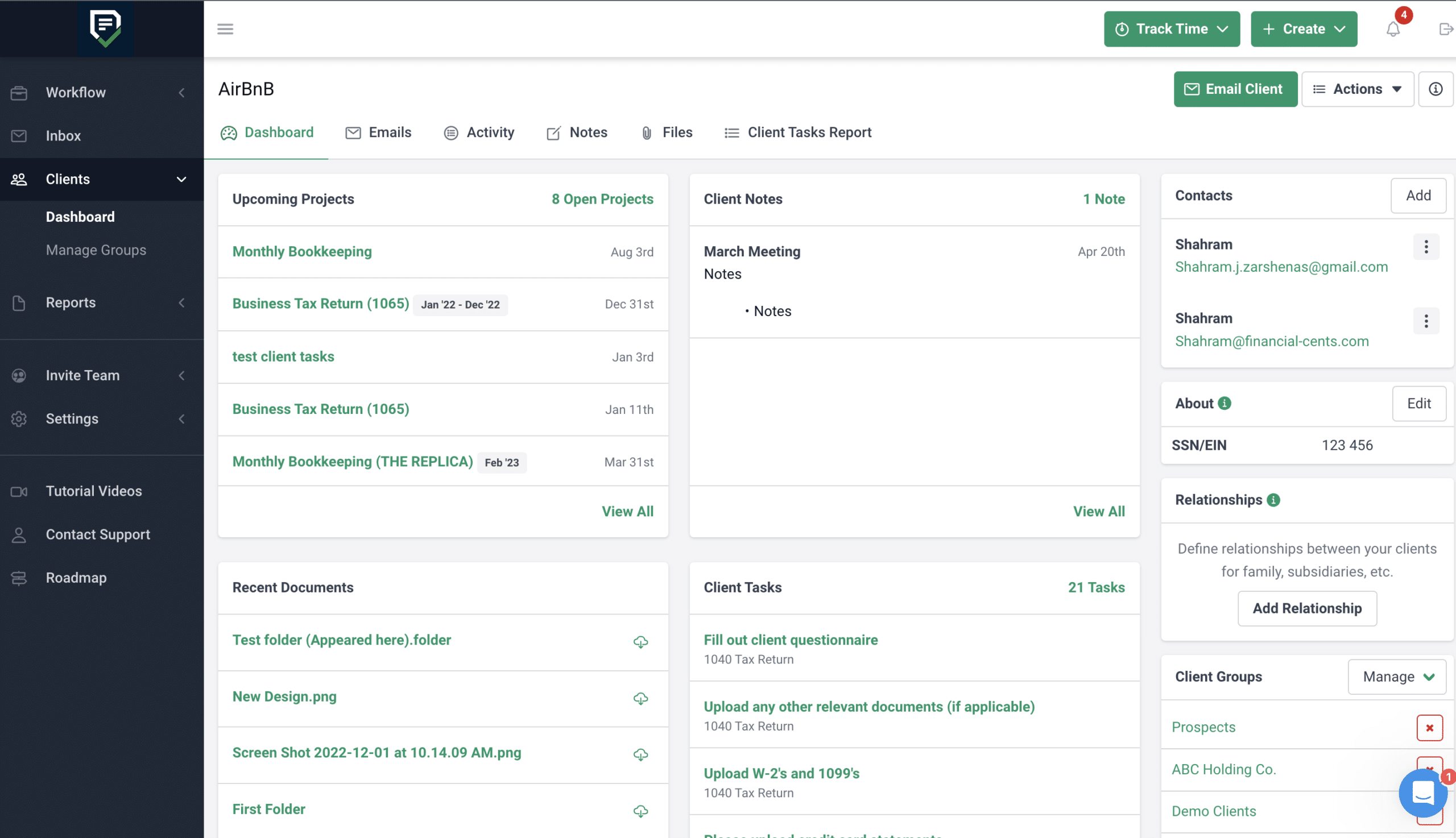
Integrating CRM and accounting modules lies at the heart of maximizing operational efficiency and maintaining accurate, up-to-date business records. The process involves connecting two or more systems to ensure seamless data flow, which reduces duplication and enhances visibility.
Common Integration Challenges and Solutions
Despite the benefits, integration can present technical and organizational challenges. Here is a detailed table outlining typical aspects, issues, and resolution strategies:
| Integration Aspect | Description | Typical Issues | Resolution Strategies |
|---|---|---|---|
| Data Mapping | Aligning fields and formats between CRM and accounting systems. | Inconsistent data types, missing fields, mapping errors. | Establish field standards and use middleware to automate mapping. |
| Process Automation | Automating workflows across platforms. | Workflow conflicts, duplicate transactions, process gaps. | Document workflows, test integrations, and set clear process rules. |
| Security Controls | Ensuring secure data transfer and access controls. | Unauthorized access, data breaches, compliance risks. | Implement role-based permissions and encrypted data exchanges. |
| Data Synchronization | Keeping records updated in real-time between systems. | Lag times, data inconsistency, sync failures. | Use robust APIs, schedule sync intervals, and monitor exceptions. |
Importance of Real-Time Data Synchronization, Crm accounting
Real-time data synchronization ensures that all teams—whether sales, finance, or management—have consistent, up-to-date information. This reduces errors, improves collaboration, and enables quick responses to customer inquiries or financial changes.
Use Cases of CRM Accounting Across Industries
CRM accounting systems are versatile and adaptable, making them valuable across a wide range of industries. Each sector leverages specific features and workflows to address unique operational challenges and regulatory requirements.
Industry-Specific Applications
The following list highlights how different sectors utilize CRM accounting:
- Retail: Tracks customer purchases, manages loyalty programs, and automates invoicing for wholesale clients.
- Services: Schedules recurring billing, manages project-based invoicing, and centralizes client histories for account managers.
- Manufacturing: Integrates order processing with accounts receivable, automates billing for large contracts, and tracks payment milestones.
- E-Commerce: Syncs online transactions with accounting, automates tax calculations, and analyzes customer purchasing trends for targeted marketing.
Industry Requirements Shaping Configurations
For example, a manufacturing firm may prioritize detailed cost tracking for each production batch, requiring tight integration between inventory, sales, and accounting. In contrast, a service provider might need automated recurring invoices and time-based billing to accommodate client retainers and project work.
Workflow Automation in CRM Accounting
Workflow automation is a hallmark of modern CRM accounting systems, driving efficiency and reducing human error. By automating repetitive and time-consuming tasks, organizations can focus on higher-value activities and deliver a better customer experience.
Typical Automated Processes
Automation in CRM accounting commonly covers processes such as:
- Invoicing clients based on completed sales or service milestones.
- Sending payment reminders for overdue accounts.
- Reconciling transactions between sales and accounting records.
- Automated report generation for management and compliance needs.
Automating workflows in CRM accounting not only streamlines operations but also boosts productivity, allowing teams to spend more time on strategic growth and customer engagement.
Security and Compliance in CRM Accounting
Security is a top priority for CRM accounting solutions due to the sensitive nature of financial and customer data. Compliance with regional and global regulations is equally important to protect both the business and its clients.
Key Security Measures and Compliance Standards
The following table presents core security practices, their purposes, implementation methods, and relevant compliance references:
| Practice | Purpose | Implementation | Compliance Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Data Encryption | Protects sensitive data during storage and transmission. | Use SSL/TLS protocols and encrypted databases. | GDPR, PCI DSS |
| Access Controls | Restricts user access based on roles and responsibilities. | Configure user permissions and two-factor authentication. | SOC 2, SOX |
| Audit Logging | Monitors user activities to detect unauthorized actions. | Implement activity logs and regular audits. | GDPR, ISO 27001 |
| Data Backup & Recovery | Ensures business continuity in case of data loss. | Schedule automatic backups and test recovery processes. | ISO 22301 |
Relevant Compliance Standards
CRM accounting platforms must adhere to regulations such as GDPR for data privacy, PCI DSS for payment data, and region-specific financial reporting requirements. These standards guide how customer and financial data should be managed, stored, and transferred.
Customization and Scalability of CRM Accounting Solutions
Customization and scalability are essential aspects for businesses aiming to adapt their CRM accounting systems as they grow and evolve. Flexible platforms allow organizations to tailor user experiences and functionality to better suit their specific workflows and reporting needs.
Customization Options in CRM Accounting
Modern CRM accounting solutions offer a range of customization options, including configurable fields, adaptable workflows, and personalized dashboards. Users can tailor invoice templates, automate unique approval processes, and create custom data views to match their business operations.
Scalability Features for Growing Businesses
Scalable CRM accounting platforms support additional users, higher transaction volumes, and the integration of new tools as companies expand. This is crucial for startups that may begin with basic features but require more advanced analytics or multi-currency support as they enter new markets.
Tailoring Reports and Dashboards

Businesses can modify reporting tools to generate insights relevant to their industry or management style. For example, a company may configure a dashboard to highlight key performance indicators (KPIs) such as cash flow, customer lifetime value, or overdue invoices, ensuring decision-makers have immediate access to the data that matters most.
Selection Criteria for CRM Accounting Software
Choosing the right CRM accounting solution is a strategic decision that can impact business efficiency, growth, and profitability. A thoughtful evaluation process ensures the chosen system aligns with organizational goals and operational requirements.
Key Factors to Consider
The table below Artikels crucial criteria, their importance, considerations, and example questions to guide vendor discussions:
| Criteria | Importance | Considerations | Example Questions to Ask Vendors |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ease of Integration | High | Compatibility with existing systems, API availability. | Does your software connect natively to our current CRM or ERP? |
| User Experience | Medium | Intuitive interface, training requirements. | How long does it typically take to onboard new users? |
| Scalability | High | Capacity to support business growth and additional users. | Can the system handle increased transaction volumes as we expand? |
| Support Services | Medium | Availability of technical support, documentation, user community. | What support channels do you offer and what are your response times? |
| Pricing Model | High | Subscription vs. perpetual, cost predictability, included features. | Are there additional fees for upgrades or integrations? |
Impact of Pricing and Support on Long-Term Value

Beyond upfront costs, ongoing support and flexible pricing can significantly affect the overall value of a CRM accounting investment. Businesses should consider not just the initial purchase price, but also maintenance fees, upgrade policies, and the vendor’s commitment to customer success.
Best Practices for Implementing CRM Accounting Systems
A successful CRM accounting implementation requires organized planning, effective training, and ongoing support. Following best practices ensures the transition is smooth and the organization realizes the full benefits of its investment.
Checklist for Implementation
A practical checklist for deploying CRM accounting systems covers the following critical areas:
- Develop a clear implementation plan with defined goals and timelines.
- Engage key stakeholders from finance, sales, and IT early in the process.
- Conduct thorough user training and offer continuous learning opportunities.
- Perform comprehensive data migration, including validation and cleanup.
- Test workflows and integrations before going live.
- Establish ongoing support and feedback mechanisms for continuous improvement.
Role of User Adoption and Continuous Improvement
Encouraging user adoption through accessible training and responsive support greatly increases the likelihood of success. Regularly gathering feedback and adapting workflows help refine the system to better fit evolving business needs and maximize return on investment.
Visualizing CRM Accounting Data
Effective data visualization is crucial in CRM accounting, enabling businesses to interpret complex financial and customer information quickly. Visual tools transform raw data into actionable insights that drive decision-making and strategic planning.
Types of Dashboards and Reporting Tools
CRM accounting systems offer various dashboards and reporting options tailored for different users, such as sales teams, finance managers, or executive leadership. Customizable dashboards might display metrics like sales pipeline value, outstanding receivables, payment statuses, or customer profitability on a single, interactive screen.
Common Graphical Representations in CRM Accounting
Graphical tools enhance the understanding of key data sets with visuals, including:
- Bar and Line Charts: Compare revenue, expenses, or invoice statuses over specific periods.
- Pie Charts: Illustrate the distribution of expenses, income sources, or customer segments.
- Heatmaps: Quickly spot trends in payment delays or identify high-value customer clusters.
- Tables and Scorecards: Present detailed, sortable lists for tracking KPIs or compliance checks.
For instance, a finance manager might use a dashboard combining a revenue trend line chart with a real-time list of overdue invoices to prioritize collection efforts, while sales leaders rely on pie charts to assess customer segment contributions to total sales.
End of Discussion
Bringing together customer relationship management and accounting, crm accounting provides businesses with a powerful toolkit to simplify complex processes and drive better decision making. As companies face ever-changing demands and opportunities, choosing the right crm accounting solution will be key to maintaining agility, security, and long-term growth. Embracing this technology means your business can work smarter, faster, and with greater confidence.
Key Questions Answered
What is crm accounting?
crm accounting is the integration of customer relationship management (CRM) tools with accounting software, allowing businesses to manage customer interactions and financial operations in one system.
How does crm accounting benefit small businesses?
It improves efficiency by automating routine accounting tasks, centralizing customer data, and enabling faster, more informed financial decisions, which is especially valuable for small businesses with limited resources.
Is crm accounting secure for handling sensitive financial data?
Most crm accounting systems include robust security features like encryption, user access controls, and compliance with industry regulations to protect sensitive financial information.
Can crm accounting software integrate with other business tools?
Yes, many crm accounting solutions offer integrations with popular email, e-commerce, payment, and analytics tools to create a connected business ecosystem.
Do all businesses need crm accounting?
While not every business requires crm accounting, those seeking to streamline customer and financial management, automate workflows, and achieve better reporting will find it highly beneficial.
