business inventories and sales are the heartbeat of any thriving company, influencing everything from cash flow to customer satisfaction. Understanding how these two fundamental elements interact can transform the way organizations operate and make decisions. Whether you’re managing a bustling retail store or a complex supply chain, mastering the balance between what’s in stock and what’s selling is key to lasting business success.
This topic explores the essential types of inventories businesses hold, popular inventory management methods, and best practices for tracking sales efficiently. It delves into how changes in inventory levels directly affect sales performance, the importance of inventory turnover ratios for evaluating efficiency, and the role of technology in streamlining operations. By the end, you’ll have a clear picture of the challenges, regulatory factors, and innovative solutions that shape business inventories and sales today.
Business Inventories and Sales Overview
Business inventories and sales are fundamental concepts that shape how companies operate, strategize, and thrive in competitive markets. An inventory consists of all the goods and materials a business holds for the purpose of resale or production, while sales represent the revenue-generating transactions where these goods or services are transferred to customers. Understanding and managing both aspects is crucial for ensuring that a business not only meets demand but also maintains optimal operational costs and maximizes profitability.
Tracking inventories and sales is essential for business success because it enables organizations to plan effectively, avoid bottlenecks, and respond proactively to market changes. When businesses closely monitor these metrics, they can make informed decisions about purchasing, production, and sales strategies, directly impacting cash flow, customer satisfaction, and long-term growth.
Definitions and Business Impact
Inventory management involves maintaining the right balance between too much and too little stock, which directly influences sales capabilities and cash flow. Sales metrics, on the other hand, provide real-time feedback on market demand and performance. Together, these metrics help businesses make strategic decisions such as when to reorder products, which items to discount, or how to allocate resources for marketing campaigns. Ineffective management can lead to missed sales opportunities or excessive carrying costs, both of which can undermine business performance.
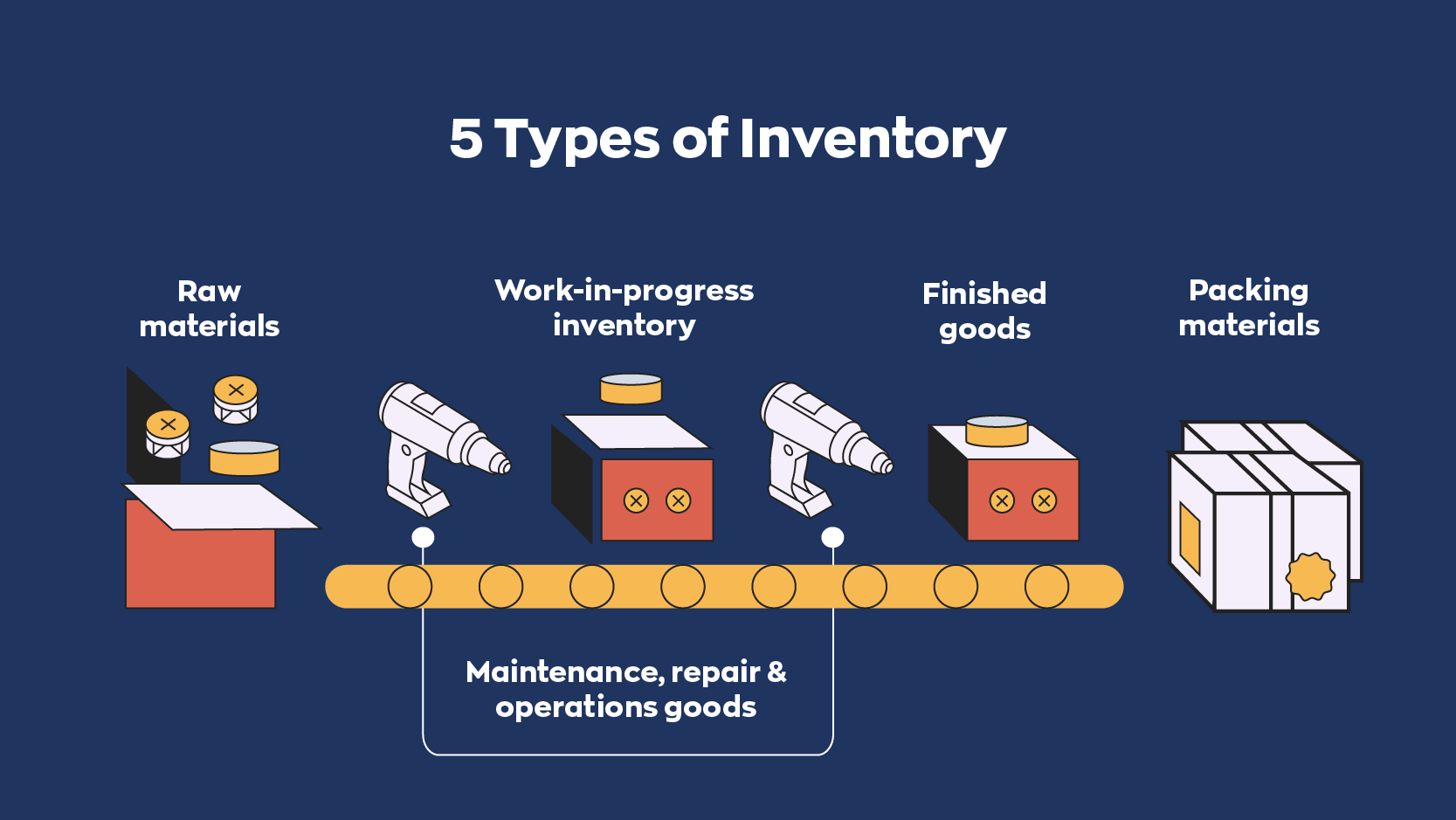
Types of Business Inventories
Inventories can be categorized into several types based on their position in the production and sales process. Each type serves a specific purpose and comes with unique handling and storage requirements. Understanding the distinctions between raw materials, work-in-progress (WIP), and finished goods is key for effective inventory control in any industry.
Main Inventory Categories
The table below Artikels the principal types of business inventories, offering a snapshot of their characteristics, industry examples, and typical storage needs.
| Inventory Type | Description | Industry Examples | Storage Requirements |
|---|---|---|---|
| Raw Materials | Basic materials used in the production process before any transformation. | Automotive (steel, rubber), Textiles (cotton, wool), Electronics (semiconductors) | Dry, secure, sometimes climate-controlled to prevent degradation |
| Work-in-Progress (WIP) | Items partway through the manufacturing or assembly process. | Furniture manufacturing (partially assembled chairs), Electronics (circuit boards), Food processing (semi-cooked products) | Accessible for quick movement, protected from contamination or loss |
| Finished Goods | Products completed and ready for sale or shipment to customers. | Retail (clothing), Technology (smartphones), Automotive (completed vehicles) | Organized, often requires packaging, may need security or temperature control |
| Maintenance, Repair, and Operations (MRO) | Supplies used in production but not part of final product. | Manufacturing (lubricants, cleaning supplies) | Easy access, safety compliance, appropriate labeling |
Methods of Inventory Management
Businesses implement various methods to manage inventory efficiently, each with unique advantages and challenges. Selecting the right inventory management method can significantly affect cash flow, tax liability, and responsiveness to market trends.
Inventory Management Approaches
Inventory management strategies are designed to address different business needs, product types, and market conditions. The three most prevalent methods—FIFO, LIFO, and Just-In-Time—are described and compared below.
| Method | Benefits | Drawbacks | Typical Use Cases |
|---|---|---|---|
| FIFO (First-In, First-Out) | Simplifies bookkeeping; matches older cost with current revenue; reduces risk of obsolescence. | May overstate profits during inflation; higher tax liability in some regions. | Grocery, pharmaceuticals, perishable goods |
| LIFO (Last-In, First-Out) | Matches latest costs with current sales; can reduce taxable income during inflation. | Not accepted under IFRS; can result in outdated inventory remaining unsold. | Some U.S. retailers, non-perishable goods |
| Just-In-Time (JIT) | Lowers inventory holding costs; increases efficiency; reduces waste. | Highly sensitive to supply chain disruptions; requires precise demand forecasting. | Automotive, electronics manufacturing |
Sales Tracking and Documentation: Business Inventories And Sales
Accurate sales tracking is crucial for assessing business performance, forecasting demand, and ensuring compliance with financial regulations. Sales documentation typically includes records of all transactions, customer details, quantities sold, and revenue generated.
Sales Tracking Records, Business inventories and sales
A comprehensive sales tracking system records each transaction in detail, supporting both daily operations and strategic planning. The following is a basic structure for a sales tracking sheet, which businesses can adapt to their specific needs.
| Date | Product | Quantity Sold | Total Revenue |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2024-04-01 | Wireless Headphones | 50 | $3,500 |
| 2024-04-01 | Laptop Sleeve | 30 | $900 |
| 2024-04-02 | Wireless Mouse | 40 | $1,200 |
Maintaining clean and accurate sales records supports better inventory planning, simplifies tax preparation, and helps identify trends. Best practices include daily updates, regular audits, and backing up digital records to prevent data loss.
Epilogue
In summary, business inventories and sales are closely linked drivers of operational excellence, profitability, and strategic planning. By mastering inventory management, employing effective sales tracking, and utilizing technology, businesses can avoid common pitfalls and capitalize on growth opportunities. Keeping a watchful eye on these elements not only ensures smooth day-to-day operations but also builds a solid foundation for future success in an ever-evolving marketplace.
Clarifying Questions
What is the difference between inventory and sales?
Inventory refers to the goods and materials a business has on hand for sale or production, while sales represent the exchange of those goods or services for revenue.
Why is tracking inventory important for a business?
Tracking inventory helps businesses prevent overstocking or running out of products, optimize cash flow, reduce losses from spoilage or obsolescence, and improve customer satisfaction.
How often should a business perform inventory counts?
Businesses should perform inventory counts at least annually, but many conduct counts quarterly, monthly, or even use real-time tracking depending on their size and industry.
Can small businesses benefit from inventory management software?
Yes, even small businesses can gain efficiency, accuracy, and better insights by using inventory management software, reducing manual errors and saving time.
How does seasonality affect inventory and sales management?
Seasonality can lead to spikes or drops in demand, requiring businesses to carefully plan inventory levels to meet customer needs without overcommitting resources.
